top of page

Fu-Lai Wen, Ph.D.
Assistant Professor
Department of Physics, NCU, Taiwan




Project 01 | Modeling geometrical trajectories of actin-based motility
Listeria monocytogenes is a pathogenic bacterium which utilizes polymerization of protein actin to power its transportation inside the host cells. Various geometrical trajectories such as straights, S-curves, and circles have been observed in experiments. Similar results have also been found in the biomimetic experiments on beads, disks, and lipid vesicles. In this project, I aim to explore the physical mechanisms responsible for generating the geometric shapes of actin-propelled trajectories.





Project 02 | Exploring the physical mechanisms underlying epithelial tissue morphogenesis
Epithelial cells are polarized along their apical-basal axis and connected with one another, forming sheets of cells that widely cover the animal body surfaces. During embryonic development, a simple epithelial sheet undergoes a series of complex deformation such as folding and twisting, leading to the formation of optic cups, neural tubes, branches of lungs, etc. In this project, I aim to explore the physical mechanisms underlying the morphogenetic development of epithelial tissues.

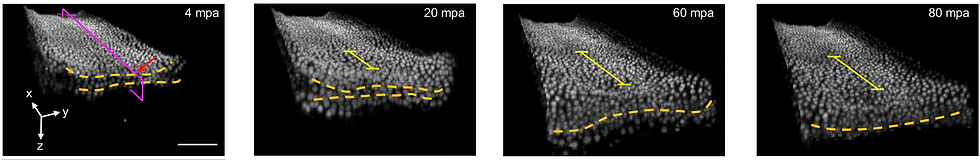


Project 03 | Identifying the biophysical principles of wound healing
Many animals in nature have the capability of healing wounds when they get injured. Understanding of the biophysical principles underlying wound healing is key to advance the medical cares for prevention of infection during healing process. Taking the advantage of zebrafish as an excellent model system for wound-healing study, in this project we aim to identify how cells collectively migrate and heal wounds during healing process, using the techniques of bio-image analysis and mathematical modeling.

Project 04 | Understanding the mechano-response of tissues
Cell and tissue dynamics are closely linked to their biological functions, and intimately regulated by the signaling factors, including biochemicals and biomechanics, from the surrounding environment. In this project, we aim to understand how cells and tissues sense, respond to, and modify the physical properties of their surroundings.
bottom of page